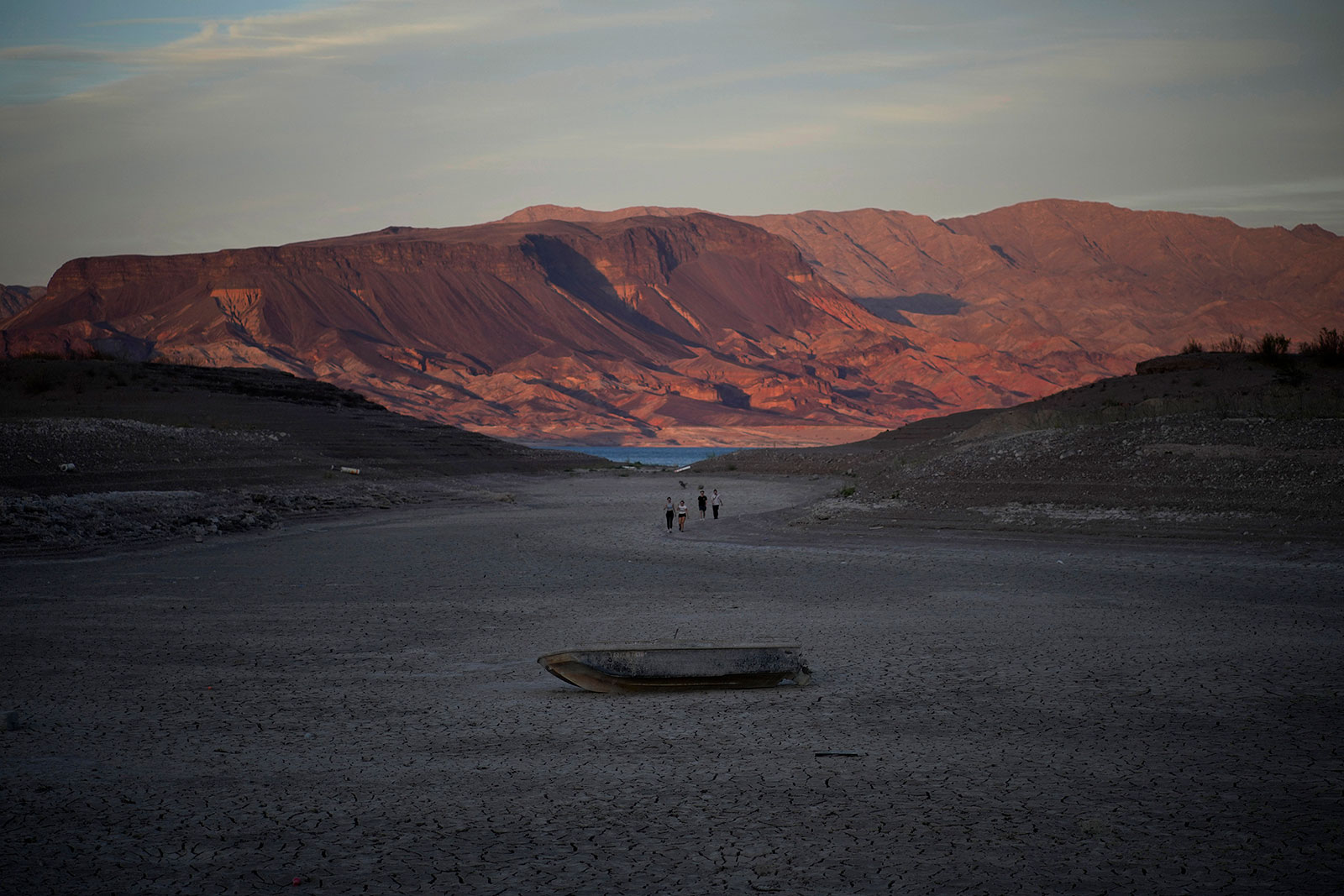

The federal government announced Tuesday the Colorado River will operate in a Tier 2 shortage condition for the first time starting in January as the West’s historic drought has taken a severe toll on Lake Mead.
According to a new projection from the Department of the Interior, Lake Mead’s water level will be below 1,050 feet above sea level come January — the threshold required to declare a Tier 2 shortage starting in 2023.
Lake Mead’s level has been around 1,040 feet this summer, just 27% of its full capacity.
The Tier 2 shortage means Arizona, Nevada and Mexico will have to further reduce their Colorado River use beginning in January. California will not yet have cuts made to the water it receives from the Colorado River. (The threshold for California’s first cut is 1,045 feet in January.)
Of the impacted states, Arizona will face the largest cuts — 592,000 acre-feet — or about 21% of the state’s yearly allotment of river water.
“Every sector in every state has a responsibility to ensure that water is used with maximum efficiency. In order to avoid a catastrophic collapse of the Colorado River System and a future of uncertainty and conflict, water use in the Basin must be reduced,” Interior’s assistant secretary for water and science Tanya Trujillo said in a statement.
Interior’s projections show that by January of next year, Lake Mead’s water surface elevations will be at 1,047.61 feet. Meanwhile, Lake Powell’s water surface elevation will be at 3,521.84 feet – 32 feet above minimum power pool, or the amount needed to generate electricity from hydroelectric operations.
Separately, US Bureau of Reclamation Commissioner Camille Touton and other federal water officials said they are prepared to take additional administrative actions needed to protect the Colorado River, Lake Powell and Lake Mead from falling to “critically low levels.”
Earlier this summer, Touton set a deadline of mid-August for the seven Colorado River states to come up with a plan to cut as much as 25% of their river water usage. It became apparent early this week that those negotiations have stalled, which led some lawmakers and state water officials to call on the federal government to take aggressive action on their own.
Interior has not yet outlined next steps in Touton’s demand for the states’ plan.





More News
Senate Approves Aid for Ukraine and Israel, Sending It to Biden’s Desk
Opinion | Well, it’s Groundhog Day … again
Opinion | How Biden can court Vietnam — and help those stuck behind bars